CONTINUATION OF INDIA-IRAN RELATIONS (5:10 PM)
- After 2003, the secret nuclear plan for Iran came into the news.
- The USA then tried to convince India to end relations with Iran.
- The US asked India to vote against Iran in the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) platform, follow American sanctions on Iran, and impose sanctions on Iran.
- India voted against Iran in the IAEA, but India did not impose sanctions on Iran and held that India would only follow UN sanctions and not of any single country.
- India reduced Iranian oil imports and started conducting the imports in domestic currency.
Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA):
- It was signed in 2015 between Iran, P5 countries, and Germany.
- It was also called the Iran Nuclear Deal.
- As per the deal, Iran accepted certain restrictions over its nuclear program and got relaxation from secondary sanctions.
- Iran agreed to eliminate its stock of medium-enriched uranium.
- Iran agreed to reduce its low-enriched uranium by 98% and gas centrifuges by 2/3rd.
- Iran agreed to give access to IAEA inspectors into its nuclear sites.
- Iran wanted to get relief from the economic sanctions.
Reasons why the USA went for the deal:
- The rise of many terror outfits like ISIS in the region.
-
USA's role in the inception of ISIS:
- The US’s key role in oustering Saddam Hussein was instrumental in creating a power vacuum within the Middle Eastern region, thus setting the stage for the rise of ISIS amidst the devastation and chaos of Iraq post-war.
- This, further complicated in the Arab Spring in 2011 with several autocratic regimes in the Sahel region toppled, enabled ISIS to find crucial support among young disillusioned youth who were out of work and disdainful of the West.
- After the fall of the Gaddafi regime in Libya, the region was left without a strong leader, hence many insurgent groups emerged in the region that also had members of disbanded militias.
- The Western world saw many citizens go to Iraq-Syria to fight ISIS; India saw very few such migrations.
- Many of those who did not go, became lone-wolf attackers in their respective countries.
- America did not want to send its army to the region again due to public opinion against the war.
- The USA later entered into a deal with Iran and joined hands with Iran against ISIS.
IMPACT ON IRAN-INDIA RELATIONS (5:40 PM)
- After the removal of sanctions, the pressure on India-Iran relations was reduced.
- India and Iran concluded in 2016 an MOU to develop the Chabahar Port.
- The U.S. in 2018 under Donald Trump 2018 pulled out of JCPOA and announced that it would now maximize pressure on Iran by reinforcing secondary sanctions.
-
Trump gave reasons:
- I. The JCPOA was anyways temporary.
- II. The deal does not stop Iran from engaging in proxy warfare.
- III. Iran violated the related IAEA guidelines.
- The USA gave 8 months time to India & China who were major importers of Iranian oil to reduce their oil imports to zero.
- By May 2019, India zeroed out its Iranian oil imports.
- Between 2015 and May 2019, Indian oil imports from Iran stood at 11% of Indian total oil imports.
- During this period, India's total trade with Iran stood at $17 billion.
- Between 2003 and 2015, India did not accept secondary sanctions from the USA and during the Trump administration, India succumbed to the US pressure.
- The India-Iran rupee-rial mechanism was also suspended.
- Iran paid for the insurance of oil imports, which is usually paid for by the importer.
- Iranian oil is also of good quality, and more suitable for Indian refineries.
- India hence got a good quality oil at competitive prices.
- Also, The USA abandoned Obama's policy of Co-op and started the policy of putting maximum pressure on Iran.
Pieces of evidence of maximum pressure by the USA:
- The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) of Iran was identified as a terrorist organization.
- It was the first time another country's army had been designated as a terrorist organization.
- America killed Qasim Solemani, the founding commander of the Quds Force in 2020 through a drone attack, and also took public responsibility.
- Qasim was instrumental in American action against ISIS.
Iranian response:
- Iran made its proxy Houthis attack Saudi oil facilities, which were under the security protection of the USA.
- As the USA did not intervene, Saudi knew that it could no longer rely on the USA for its security.
- Iran shot down American drones over the Strait of Hormuz.
- Iran threatened to shut done the Strait of Hormuz.
-

- Trump's strategy did not bear much result.
- When Joe Biden came to power, he indicated his willingness to re-enter JCPOA.
- However, by this time the moderate government in Iran was replaced by a more rightist/conservative government.
- Iran and the USA have not been able to re-negotiate rejoining JCPOA.
- JCPOA is dead for all practical purposes.
INDIA-IRAN PRESENT RELATIONS (6:10 PM):
- After India joined secondary sanctions on Iran and zeroed out its oil imports, Iran conducted a cost-benefit analysis of its relations with New Delhi.
- It realized India needs Iran more than Iran needs India.
- Iran is critical for New Delhi's connectivity to Afghanistan, Central Asia, and Europe as well.
- After no Indian oil imports, Iran did not have much to lose in its relations with India.
- Thus, there was a deterioration in the bilateral ties.
- They have made efforts to once again revive cooperation after 2021.
- There have been high-level visits between the two countries.
- PM Modi said that India -Iran relations have "strong historical & civilizational connections including strong people-people contact".
Challenges in India-Iran relations:
I. American sanctions on Iran impede oil imports.
- In 2018, 11% of Indian oil imports came from Iran.
- Oil import diversification is important for India because:
- I. India is an emerging economy with 80% of its oil requirements met through imports.
- Recent fluctuations in oil prices due to the Russia-Ukraine war.
- Being a large il-importer, India remains susceptible to such price fluctuations.
- Higher oil prices during the First Gulf War in 1990 were the main reason behind the only Balance of Payments crisis that India faced in 1991.
- Indian crude oil imports from the USA, Iraq, Saudi Arabia & UAE roughly account for 63% of the value of total crude oil imports.
- Indian bilateral trade with Iran now stands at around $2 billion, when the Rupee-Rial mechanism for oil imports is suspended.
II. Kashmir Issue:
- Iran adopts a pro-Pakistan stance on it
III. China factor:
- Due to American secondary sanctions, the Chinese share in Iranian oil exports has risen from 25% to 45 %.
- The Iranian economy is hence dependent on China.
- China has become the largest trade partner of Iran.
- China & Iran have concluded a deal whereby China has promised $400 billion in investments in Iran over the next 25 years.
- The largest beneficiary of the American sanctions has been China, as China circumvents American sanctions.
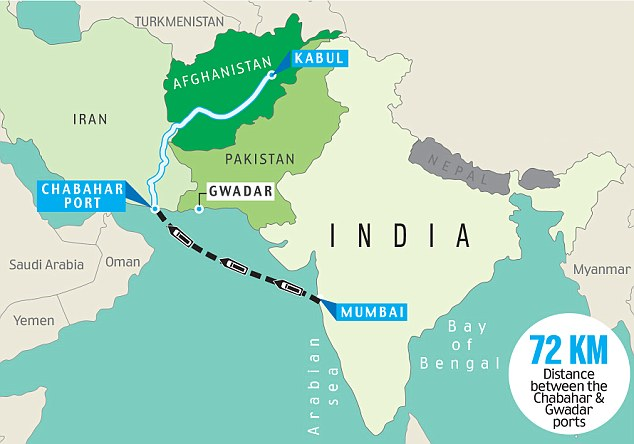
- Indian plan to develop Chabahar port was to counter the Chinese development of Gwadar port in Balochistan province.
-
IV. India joining I2U2:
- The rest three countries have bad relations with Iran.
V. Domestic situation in Iran:
- Severe economic crisis due to depreciating currency Rial.
- The orthodox government and deployment of Moral Police pressurises women to cover their faces in public.
- Iranian women continue to resist.
POINTS OF CONVERGENCE (6:40 PM):
I.Afghanistan:
- In the past, India and Iran have collaborated over Afghanistan.
- Iran presents an alternative land route to Afghanistan.
- Both countries want an inclusive government representing all spectrum of the Afghan society and peace in Afghanistan.
II. Iranian Nuclear Deal:
- It is dead for all practical purposes.
- This means the sanctions on Iran will continue.
- India can explore a stand similar to the one it adopted concerning Western sanctions on Russia.
- This could open huge potential for trade in oil and other goods.
III. Ongoing rebalancing in West Asia:
- Evidences:
- I. Abraham Accords through which UAE, Bahrain, Morocco, and Sudan have normalized their ties with Israel.
- II. Iran and Saudi Arabia reopening their embassies in each other's countries after 7 years, after Chinese mediation.
- This creates an opportunity for India to engage in mutually beneficial partnerships with all the major countries of the region.
Way Forward:
- India is a leading power with global power ambitions and cannot succumb to the pressure of a third country to pursue its relations with other nations.
- So India should adopt an autonomous need-based foreign policy with respect to Iran.
- India should convey its strategic concerns with Iran to the USA and how American secondary sanctions are in fact benefitting China in the region.
- India should consider restarting oil imports from Iran.
- INSTC corridor though operationalized in parts has not been able to achieve its full potential because of sanctions on Iran.
- So India should explore giving a boost to the INSTC to reap resultant trade benefits.
- Iranian SCO membership creates more avenues for multilateral engagement with Iran.
- Iran-Oman-India gas pipeline:
- Iran and Oman signed a deal in 2022 to develop two gas pipelines and an oil field along their maritime borders.
-

- If the deal is realized, there would be potential for the pipeline to be extended to India.
- It would help to overcome the loss of the failed Iran-Pakistan-India pipeline.
IRAN-SAUDI ARABIA PEACE DEAL (7:10 PM):
- The deal has been brokered by China.
- The embassies were closed after protests that followed the Saudi execution of a Shia cleric in 2016.
- Iran agreed not to sponsor Houthi attacks on oil facilities in southern Saudi Arabia.
- Saudi promised to tone down Iran International, a Farsi news channel that is critical of the Iranian regime.
- The deal is said to be a low-cost (because both countries wanted normal relations), high-opportunity deal (all such deals in the region were brokered by the USA).
- Saudi Arabia entered the deal under its Vision 2030 for which it wishes to focus on economic development and technology.
- Iran entered the deal to overcome its economic problems and domestic issues.
- Iran is also hoping for Chinese investments, including the $20 billion that remains frozen in China due to sanctions.
- China brokered the deal because it seeks to expand its influence in West Asia.
- American Reaction:
- It expects good results and peace from the deal.
- Indian Reaction:
- India has not expressed its opinion as such but it hopes that if the deal brings peace to the region, Indian interests in the region will get smooth.
- India is also expected to gain if Chinese influence increases in the region as India is seen as a balancing power to China.
NUCLEAR TREATIES (7:30 PM):
Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT):
- It was adopted in 1968 and it entered into force in 1970.
- In an NPT review conference in 1995, the treaty was extended indefinitely.
- It is referred to as a cornerstone of the global nuclear order.
Aims of the treaty:
- Nuclear non-proliferation.
- Promoting the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
- Global nuclear disarmament; is a weak aim as no timeline or process is mentioned for this.
Working of the treaty:
- It classifies countries as Nuclear Weapon States (NWS) and Non-Nuclear Weapon States( NNWS).
- Those countries that have tested their nuclear weapons by 1st January 1967 are mentioned in NWS.
- As a matter of coincidence, all the P5 countries (The USA, The UK, France, Russia & China) are classified as NWS.
- All rest countries are classified as NNWS.
- If NNWS agrees to not develop nuclear weapons, NWS will share peaceful nuclear technology.
There were issues with this provision:
- Nuclear technology is a dual-use technology- can be used both for energy and weapons.
- Iran and North Korea used this provision to develop nuclear weapon technology.
- North Korea came out of the treaty later
- The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) was made a watchdog for the treaty.
- IAEA sends its inspectors to check if countries are developing nuclear weapons.
- China has also shared nuclear power technology with Pakistan.
Significance of the treaty:
- It is the only binding treaty that binds nuclear weapon states to disarmament.
- The treaty has been indefinitely extended after 1995.
- It has 191 signatory countries, so it has a near-universal membership and general global consensus.
- Only India, Israel, Pakistan, and South Sudan have never joined the NPT (North Korea announced its withdrawal in 2003).
- The treaty is largely successful in its aim to stop horizontal proliferation.
-
I. Vertical Proliferation:
- Increasing the number and sophistication of nuclear weapons.
II. Horizontal Proliferation:
- NNWS getting access to nuclear weapons.
- In more than 50 years since its enforcement, only four countries could develop nuclear weapons- India, Pakistan, Israel & North Korea.
- In comparison, within 2 decades of America acquiring nuclear weapons, four other states acquired them.
Indian reasons for not joining:
- The treaty is discriminatory- divides nations into NWS and NNWS.
- The treaty only checks horizontal proliferation.
- India believed in the concept of the Nth nation problem.
- This concept says that till the time even a single country possesses nuclear weapons, others will be motivated to develop nuclear weapons.
- Indian goal is universal, time-bound, verifiable, and irreversible global nuclear disarmament.
Indian chances for joining NPT:
- Being a nuclear power, India can join the NPT only if the NPT's charter is amended.
- That might encourage other nations to develop nuclear weapons as well.
- India can join if it surrenders/dismantles its nuclear arsenal.
- The option is not practical as India has a considerable threat from two nuclear-armed neighbours.
The topic for the next class is the rest of global nuclear treaties.